In the realm of digital electronics, where innovation continuously pushes the boundaries of what’s possible, it’s essential to acknowledge the foundational elements that paved the way for modern computing marvels. Among these building blocks is the Resistor Transistor Logic (RTL) circuitry, a fundamental architecture that laid the groundwork for subsequent advancements in digital circuit design.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding RTL Circuits
At its core, RTL employs resistors and bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) to perform logic functions. Developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s, RTL circuits represented a significant advancement over their predecessors, such as vacuum tube-based circuits, offering improved reliability, efficiency, and scalability.
The Anatomy of RTL
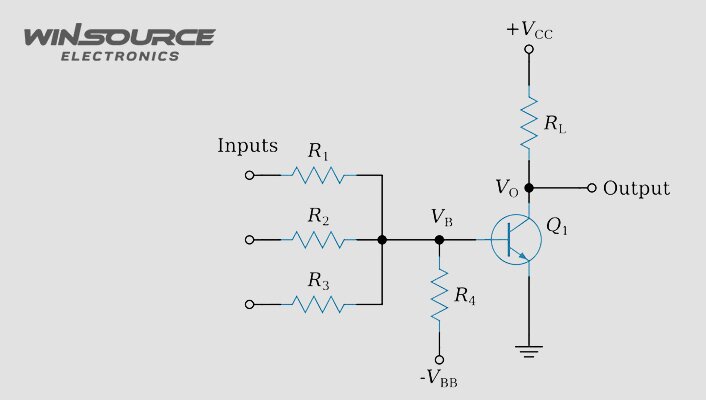
An RTL circuit typically comprises a network of resistors and transistors interconnected to implement various logical functions, such as AND, OR, and NOT gates. The arrangement of these components allows for the manipulation and processing of binary data, making RTL circuits pivotal in digital systems.
In an RTL gate:
- Resistors are used to bias transistors and establish the desired operating conditions.
- Transistors serve as the primary switching elements, controlling the flow of current based on the input signals.
- The configuration of resistors and transistors determines the logical behavior of the circuit, enabling it to perform specific operations.
Advantages of RTL
- Simplicity: RTL circuits are relatively simple in design compared to other logic families, making them easy to understand and implement.
- Low Power Consumption: Due to the absence of complex components like diodes or capacitors, RTL circuits typically consume less power, making them suitable for low-power applications.
- High Noise Margin: RTL circuits offer robust noise immunity, ensuring reliable operation even in noisy environments.
- Compatibility: Despite being an older technology, RTL circuits can interface with newer logic families, facilitating their integration into modern systems.
Applications of RTL Circuits
Despite the emergence of more advanced logic families, RTL circuits continue to find applications in various domains, including:
- Industrial Control Systems: RTL circuits are well-suited for controlling industrial processes due to their reliability and simplicity.
- Embedded Systems: In embedded applications where power efficiency is crucial, RTL circuits remain a viable choice.
- Education and Training: RTL circuits serve as excellent educational tools for teaching digital logic fundamentals to students and enthusiasts.
The Legacy and Evolution
While RTL circuits have largely been superseded by more advanced technologies like transistor-transistor logic (TTL) and complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS), their legacy endures in the annals of digital electronics. The principles underlying RTL laid the foundation for subsequent logic families, contributing to the evolution of modern computing.
In conclusion
Resistor Transistor Logic circuits stand as a testament to the ingenuity of early digital pioneers. Their simplicity, reliability, and historical significance continue to resonate in today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, reminding us of the enduring impact of foundational innovations. As we journey into the future of digital design, let us not forget the humble beginnings represented by RTL circuits—a cornerstone upon which the edifice of modern computing stands tall.

COMMENTS