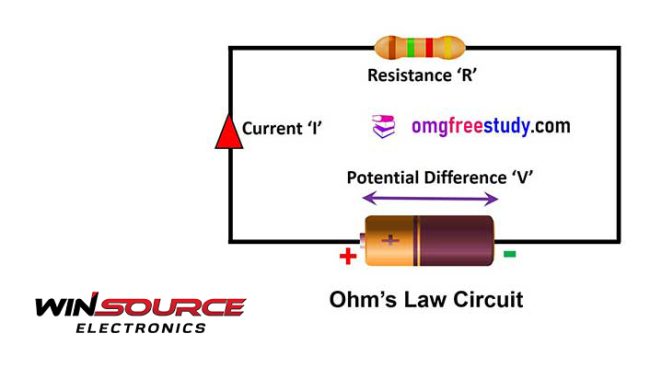
What is Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s Law, a fundamental concept in the world of electricity, is named after the pioneering work of Georg Simon Ohm, a German physicist.
Ohm’s groundbreaking research in the early 19th century led to the formulation of a simple yet incredibly powerful law that governs the behavior of electrical circuits.
This law, expressed in the equation V = I * R, lies at the heart of our understanding of electricity.
Voltage (V)
Voltage, measured in Volts, represents the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit.
It is analogous to the pressure in a water pipe; the greater the voltage, the stronger the push of electric charge.
Current (I)
Current, measured in Amperes, is the flow of electric charge through a conductor.
Think of it as the rate at which electrons move through a wire.
The higher the current, the more electrons pass a point in a given amount of time.
Resistance (R)
Resistance, measured in Ohms, quantifies the opposition to the flow of electric current.
It’s akin to the narrowing of a water pipe, where a higher resistance restricts the flow of electrons, causing them to move more slowly.
The Essence of Ohm’s Law
Now, let’s delve into the essence of Ohm’s Law.
This law tells us that the relationship between these three crucial electrical parameters can be expressed in a simple, yet profound manner:
V = I * R
In this equation, voltage (V) is directly proportional to current (I) and inversely
proportional to resistance (R). Here’s what this means in practical terms:
- Direct Proportionality: If you increase the voltage applied to a circuit, the current flowing through that circuit will increase as well, provided that the resistance remains constant. It’s similar to how opening a faucet wider allows more water to flow through it. Similarly, increasing voltage leads to a greater flow of electric charge.
- Inversely Proportional: Conversely, if you raise the resistance in a circuit while keeping the voltage constant, the current will decrease. Picture squeezing a narrow section of a water hose; the resistance increases, and the water flow diminishes. Similarly, increasing resistance in an electrical circuit restricts the flow of electrons.
Understanding this relationship is pivotal because it enables us to make precise predictions and calculations about electrical circuits.
Ohm’s Law is not just an abstract concept; it’s a practical tool that empowers engineers, electricians, and enthusiasts to design, troubleshoot, and ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical systems.
It’s the key to unlocking the mysteries of electrical circuits and harnessing the power of electricity for our technological advancements.
Examples of using The Ohm’s Law Wheel
The Ohm’s Law wheel is a handy tool for quick calculations in electrical circuits.
As we discovered above, It helps you find the value of voltage (V), current (I), or resistance (R) when you know the other two.
Here are some examples of how to use the Ohm’s Law Wheel
Finding Voltage (V):
If you want to calculate voltage and you know the current (I) and resistance (R), cover the “V” on the wheel.
The formula will reveal V = I * R. Simply multiply the given current and resistance values to find the voltage.
Finding Current (I)
When you want to determine the current and have the voltage (V) and resistance (R), cover the “I” on the wheel.
The formula underneath will be I = V / R. Divide the given voltage by the resistance to find the current.
Finding Resistance (R):
If you need to find the resistance (R) and have the voltage (V) and current (I), cover the “R” on the wheel.
The formula will show R = V / I. Divide the voltage by the current to get the resistance value.
So let’s look at another practical example.
Imagine you have a circuit with a current of 2 Amperes (I) and a resistance of 4 Ohms (R). What is the voltage (V)?
Cover “V” on the Ohm’s Law wheel.
The formula revealed is V = I * R.
Plug in the values: V = 2 A * 4 Ω = 8 Volts.
The voltage (V) is 8 Volts.
In this example, by using Ohm’s Law wheel, you easily calculated that the voltage is 8 Volts when the current is 2 Amperes and the resistance is 4 Ohms.
The Ohm’s Law wheel simplifies these calculations by providing the formula for the variable you want to find.
Ohm’s Law in Practice
The practical applications of Ohm’s Law are as diverse as the electrical systems it governs.
Understanding and applying Ohm’s Law is vital in numerous scenarios, from designing electronic circuits to ensuring electrical safety, optimizing power distribution, and troubleshooting faults.
Let’s explore some of these applications in greater detail:
- Electronics Design:For electrical engineers and hobbyists involved in designing circuits, Ohm’s Law is an essential tool. It allows them to calculate the voltage, current, and resistance needed to achieve desired performance in a circuit. Whether it’s designing a power supply, audio amplifier, or digital control system, Ohm’s Law forms the foundation for these creations.
- Electrical Safety:Electricians and those working with electrical systems must be well-versed in Ohm’s Law to ensure safety. By applying Ohm’s Law, they can calculate the expected current and voltage in circuits, which is critical for assessing the safety of installations and identifying potential hazards. This knowledge helps prevent electrical accidents and ensures compliance with safety standards.
- Power Distribution: In the realm of power transmission and distribution, Ohm’s Law plays a pivotal role. Engineers use it to design efficient electrical grids and minimize power losses due to resistive heating in transmission lines. By calculating the voltage drop across long-distance power lines, they can ensure that electricity reaches its destination with minimal energy loss.
- Troubleshooting:When electrical systems malfunction, Ohm’s Law is a valuable tool for diagnosing problems. By measuring voltage, current, and resistance at different points in a circuit, one can identify issues such as open circuits, short circuits, or faulty components. Troubleshooting with Ohm’s Law is like solving an electrical puzzle, where the known values help piece together the solution.
- Resistor Calculations:Ohm’s Law is particularly useful for selecting and configuring resistors in electronic circuits. Engineers and hobbyists can determine the appropriate resistor values to achieve specific voltage levels or current limits. This is crucial for fine-tuning the behavior of electronic devices.
- LED and Diode Circuits: Ohm’s Law is applicable when working with light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and diodes in circuits. It helps calculate the current-limiting resistors needed to ensure the diodes receive the correct current for optimal performance and longevity.
- Amplifier Design: In audio and radio frequency amplifier design, Ohm’s Law assists in selecting components such as transistors and resistors to achieve the desired voltage gain, current flow, and power output.
- Heating and Cooling Systems: When designing and troubleshooting heating and cooling systems, understanding Ohm’s Law is crucial. It helps calculate the electrical power consumed and the heat generated, which is essential for maintaining temperature control in various applications.
Demystifying Ohm’s Law – To End With…
In essence, Ohm’s Law is not confined to theoretical textbooks; it’s a practical tool used daily by professionals in various fields.
It allows us to manipulate and control electricity to meet our needs, ensure safety, and drive technological advancements.
So whether you’re designing a sophisticated electronic device, installing electrical systems, or maintaining industrial machinery, Ohm’s Law and the Ohm’s Law Wheel is the guiding principle that keeps the world powered and connected.
It’s a testament to the enduring relevance of a scientific discovery made nearly two centuries ago.
© 2025 Win Source Electronics. All rights reserved. This content is protected by copyright and may not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, cached or otherwise used, except with the prior written permission of Win Source Electronics.

COMMENTS