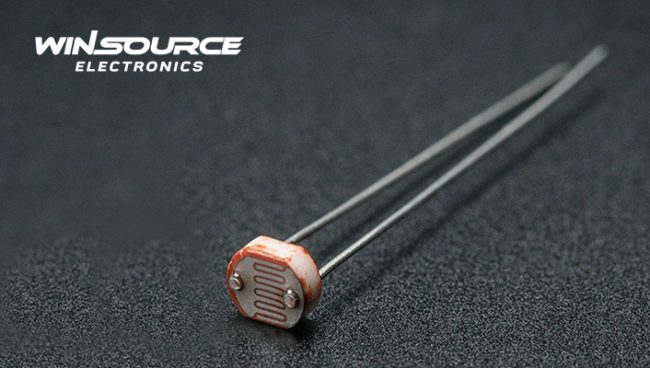
What is a photocell?
A photocell, also known as a photoresistor or light-dependent resistor (LDR), is an electronic component designed to sense and respond to changes in ambient light levels.
At its core, a photocell is a passive and light-sensitive semiconductor device that acts as a transducer, converting variations in light intensity into changes in electrical resistance.
This fundamental characteristic makes it an invaluable tool in various industry applications.
Photocells are typically produced using semiconductor materials, with cadmium sulfide (CdS) and cadmium selenide (CdSe) being common choices.
These materials have a unique property.
Their electrical conductivity changes significantly in response to the presence or absence of light.
The working principle of a photocell is elegantly simple. When exposed to light, the semiconductor material’s atoms absorb photons, which are packets of light energy.
This energy excites the electrons within the atoms, causing them to move from their lower energy state to a higher one.
This increases the semiconductor material’s resistance, making it less conductive.
In the absence of light or low light levels, the semiconductor’s atoms release the absorbed energy, returning the electrons to their lower energy state.
This results in an increased resistance in the semiconductor material, making it less conductive.
In practical terms, when a photocell is integrated into an electrical circuit, it forms a part of a voltage divider.
The photocell’s light-dependent resistance varies the voltage across it, thereby influencing the circuit’s overall voltage level.
This voltage change can be interpreted and used to trigger various actions or responses in electronic systems.
Circuit Diagram of Photocells
The circuit diagram for a photocell is relatively straightforward.
A common arrangement includes connecting the photocell in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor.
When ambient light falls on the photocell, its resistance decreases, causing the voltage across it to drop.
In contrast, low light levels increase resistance, leading to a higher voltage drop across the photocell.
To create such a circuit, you need a power source (usually a battery or a power supply), a photocell, a fixed resistor, and an output device that interprets the voltage change, like a microcontroller or an analog-to-digital converter.
What types of circuit photocells are there?
Types of Photocells
Photocells come in several variations to suit different applications:
- Cadmium Sulfide (CdS) Photocells:These are the most common type and work well for most light-sensing applications. They are cost-effective and have a wide sensitivity range.
- Cadmium Selenide (CdSe) Photocells:CdSe photocells are sensitive to a broader spectrum of light and are used in specific applications like infrared sensors.
- Phototransistors: Phototransistors are active devices that amplify the photocell’s signal. They are often employed in applications that require high sensitivity.
- Photodiodes:Photodiodes are semiconductor devices designed to convert light into electrical current. They are used in optical communication and as light detectors in various systems.
Okay so now we understand a little more about these power-packed devices, let’s find out why you might use one.
What Are Photocells Commonly Used For?
Photocells have a huge range of practical applications in various fields.
These devices change their electrical resistance in response to changes in light intensity.
Here are some of the practical applications of photocells and the users who might benefit from using them:
- Outdoor Lighting Control: Photocells are commonly used in outdoor lighting systems, such as streetlights, parking lot lights, and security lighting. They automatically switch lights on at dusk and off at dawn, saving energy and ensuring visibility at night. Utility companies, municipalities, and property owners use them to reduce electricity costs.
- Photovoltaic Systems: In solar energy systems, photocells can track the sun’s position by measuring the intensity of sunlight. Solar panels can adjust their angle to maximize energy collection, making them more efficient. This technology benefits homeowners, businesses, and utility-scale solar farms.
- Photography and Camera Exposure Control: Professional and amateur photographers use photocells in light meters to determine the correct exposure settings for their cameras. This ensures well-balanced and properly exposed photographs.
- Automatic Lighting in Indoor Spaces:In offices, warehouses, and homes, photocells are integrated into lighting systems to control artificial lighting based on the available natural light. This helps reduce energy consumption and provides a comfortable working environment.
- Security Systems:Photocells are used in security systems, where they can detect changes in light levels caused by an intruder’s movement. When this occurs, alarms can be triggered, alerting security personnel or property owners.
- Automatic Plant Growth Systems: In agriculture and horticulture, photocells are used to control artificial lighting in greenhouses. They ensure that plants receive the right amount of light for photosynthesis, growth, and flowering. Greenhouse operators and researchers use them for optimal plant cultivation.
- Consumer Electronics: Some consumer electronics, like automatic night lights and outdoor garden lighting, use photocells to turn lights on and off based on ambient light conditions, providing convenience and energy savings for homeowners.
- Weather Stations: Photocells are used in weather monitoring equipment to measure the brightness of the sky. This information is crucial for various meteorological applications and can be utilized by meteorologists and researchers.
- Traffic Control:Traffic lights and signals often use photocells to detect changes in ambient light conditions, ensuring proper signal visibility for drivers and pedestrians.
- Artificial Intelligence and Robotics: Photocells can be used in robotics for light-based navigation and sensing. Robots can adapt to changing lighting conditions, which is useful in various industries, including manufacturing and logistics.
Shedding Light on Photocells – To End On…
Photocells as we’ve discovered offer a versatile and cost-effective way to control and optimize lighting and other systems in response to changing light levels.
Users range from homeowners and photographers to businesses, agriculture, and industrial sectors, making them a valuable component in modern technology and a wealth of energy-saving applications.
For all your image-sensing needs and projects don’t forget to head over to our store to find our huge range of photocells and more.
© 2025 Win Source Electronics. All rights reserved. This content is protected by copyright and may not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, cached or otherwise used, except with the prior written permission of Win Source Electronics.

COMMENTS