* Question
What Are the Usage Rules of Arithmetic Operators in Programming?
* Answer
Arithmetic operators are used to perform basic mathematical operations in programming and control systems. To ensure correct calculation results and predictable program behavior, their usage follows a set of well-defined rules.
1. Types of Arithmetic Operators
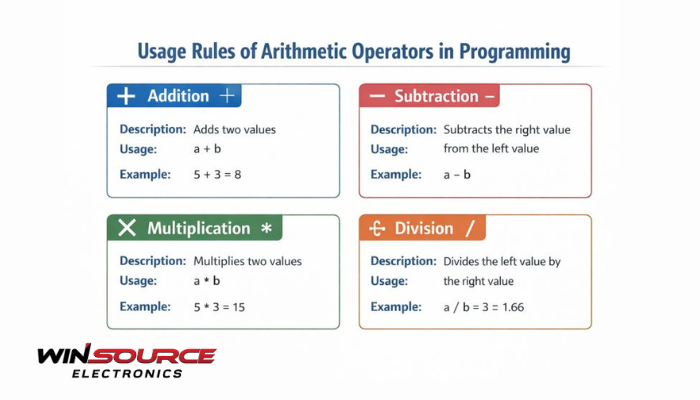
Arithmetic operators typically include:
- Addition (+)
- Subtraction (-)
- Multiplication (*)
- Division (/)
- Modulus (%, in many programming languages)
Each operator performs a specific mathematical function and must be used with compatible data types.
2. Operator Precedence
Arithmetic operators follow a fixed order of precedence, which determines how expressions are evaluated:
- Multiplication and division
- Addition and subtraction
Expressions with higher-precedence operators are evaluated first unless parentheses are used to alter the order.
3. Use of Parentheses
Parentheses () are used to explicitly define the calculation order.
They override default operator precedence and improve code readability, especially in complex expressions.
4. Operand Data Type Compatibility
Arithmetic operations are affected by the data types of their operands.
Common considerations include:
- Integer vs. floating-point division
- Type conversion and casting
- Overflow and underflow behavior
Incorrect data type handling can lead to unexpected calculation results.
5. Division and Modulus Constraints
Division operations require special attention:
- Division by zero is not allowed and typically causes runtime errors
- The modulus operator is usually defined only for integer operands
Program logic should always prevent invalid arithmetic operations.
6. Evaluation Order and Associativity
When multiple operators of the same precedence appear in an expression, evaluation follows associativity rules, typically from left to right.
Understanding associativity helps avoid ambiguous expressions and logic errors.
Summary
The usage rules for arithmetic operators include understanding operator types, precedence, associativity, data type compatibility, and safe handling of division operations. Applying these rules correctly ensures accurate calculations and reliable program behavior in software and control systems.

COMMENTS