* Question
What types of sensors are used in collision avoidance systems?
* Answer
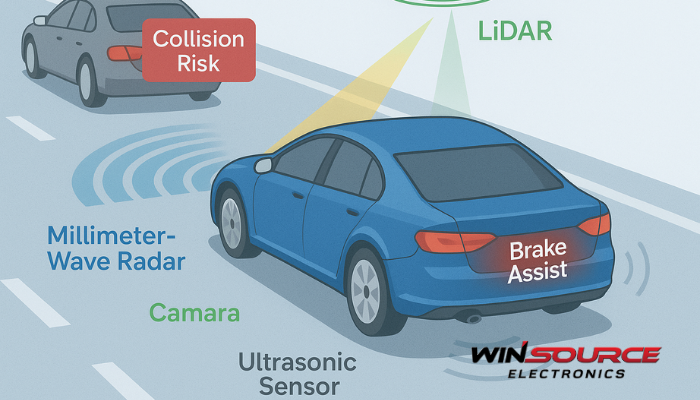
Collision avoidance systems rely on multiple types of sensors that complement each other. Here’s a clear breakdown:
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Radar Sensors
Function: Emit radio waves to detect distance, speed, and relative movement of objects.
Range: Medium to long (tens to hundreds of meters).
Use Cases: Adaptive cruise control, forward collision warning, blind-spot monitoring.
Strengths: Reliable in poor weather and low light.
Limitations: Lower resolution compared to optical sensors.
2. Ultrasonic Sensors
Function: Use high-frequency sound waves to measure the proximity of nearby objects.
Range: Very short (up to a few meters).
Use Cases: Parking assist, low-speed maneuvering, obstacle detection at close range.
Strengths: Simple, low-cost, effective in close quarters.
Limitations: Limited range, affected by surface texture and environmental noise.
3. Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging)
Function: Emit laser beams to build a high-resolution 3D map of surroundings.
Range: Short to medium (tens to a few hundred meters).
Use Cases: Autonomous vehicles, drones, advanced robotics.
Strengths: Very precise distance and shape detection.
Limitations: Expensive, affected by fog, dust, or heavy rain.
4. Cameras (Optical Sensors)
Function: Capture images for computer vision and AI-based recognition of objects, lanes, and signs.
Range: Short to long, depending on resolution and optics.
Use Cases: Lane departure warning, pedestrian detection, traffic sign recognition.
Strengths: Provide detailed contextual information.
Limitations: Sensitive to lighting and weather; require high processing power.
5. Infrared (IR) Sensors
Function: Detect heat signatures or use active IR reflection.
Range: Short to medium.
Use Cases: Night vision, pedestrian and animal detection in low-light conditions.
Strengths: Work in darkness, detect living beings.
Limitations: Limited range, less effective in high ambient temperatures.
6. Supporting Sensors (for positioning and motion)
GNSS (GPS, GLONASS, etc.): Provides location data for route planning and geofencing.
IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Tracks acceleration and rotation, improving motion prediction.
Applications: Drones, autonomous vehicles, industrial robots.
Summary:
Radar & lidar → detect range and velocity.
Cameras & IR → provide recognition and classification.
Ultrasonic → cover very short distances.
GNSS & IMU → add positioning and motion awareness.
Most modern systems use sensor fusion—combining radar, cameras, lidar, and ultrasonics—to ensure redundancy and reliability.

COMMENTS