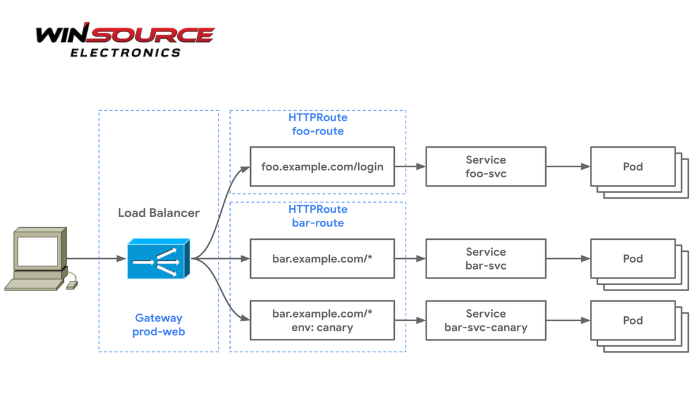
* Question
What is a write gateway session and routing?
* Answer
A write gateway session and routing generally refers to processes involved in data communication and control between systems, especially in distributed networks, databases, or embedded systems. The exact meaning can vary slightly depending on the context (e.g., IoT, networking, cloud systems), but here’s a breakdown of the typical interpretation:
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Write Gateway Session
Definition:
A write gateway session is a communication session in which a gateway device or node is responsible for accepting, processing, and forwarding data written (sent) by a client or device to a designated destination—such as a database, cloud service, or another network node.
Key Roles:
Session Management: The gateway manages secure, timed, and authenticated communication between a data source and destination.
Write Operation Handling: It receives “write” commands or payloads (e.g., sensor values, control signals) from one system and prepares them for routing or storage.
Protocol Translation: If the source and destination use different protocols, the gateway may convert data formats or message structures.
Example Use Cases:
In IoT systems, a sensor writes data to a gateway (e.g., MQTT or HTTP), which then routes it to the cloud.
In database middleware, an API gateway might handle write requests to a backend database.
2. Routing
Definition:
Routing in this context refers to the logic or process used by the gateway to determine where and how to send the incoming data. It ensures that the written data reaches the correct endpoint based on predefined rules or dynamic decisions.
Routing Responsibilities:
Address Resolution: Identifying the correct destination (e.g., server IP, database shard).
Load Balancing: Distributing write traffic across multiple targets.
Path Selection: Choosing optimal or policy-based routes (e.g., via internal networks or over the internet).
Filtering or Transformation: Applying business rules before routing (e.g., filtering invalid data).
3. Combined Process (Overview)
When combined, write gateway session and routing looks like this:
A device or user sends a write request to a gateway.
The gateway authenticates and opens a session, applies necessary preprocessing.
The gateway routes the data to the appropriate destination based on routing logic (e.g., destination address, database node, service queue).
The session may remain active (persistent) or close after completion (stateless or transactional).
Example Scenario (IoT):
Smart meter → Gateway → Cloud database
Write Session: The smart meter initiates a session with the local gateway to send energy usage data.
Routing: The gateway routes the data to the appropriate cloud endpoint, possibly tagging it with device ID, time, and location.
In summary, a write gateway session and routing refers to the process of receiving and directing write operations through a gateway that manages communication sessions and determines how to route the data efficiently and securely to its destination.

COMMENTS