* Question
What are the components of the wireless sensor network system architecture?
* Answer
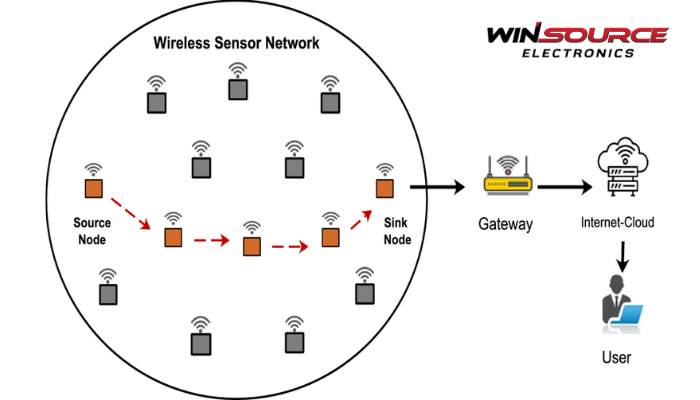
The architecture of a wireless sensor network (WSN) typically consists of several key components:
1. Sensor Nodes: These are the primary devices that collect data from the environment. They usually include:
– Sensors: For measuring physical phenomena like temperature, humidity, light, etc.
– Microcontroller: For processing sensor data and controlling the node’s operation.
– Communication Module: For transmitting data to other nodes or a central system.
– Power Supply: Typically batteries or energy harvesting systems.
2. Gateway Nodes: These act as intermediaries between sensor nodes and external networks. They aggregate data from multiple sensor nodes and transmit it to a central server or the cloud. Gateways often have more processing power and storage capacity than individual sensor nodes.
3. Data Management System: This includes the software and databases used for storing, processing, and analyzing the data collected from the sensor nodes. It may involve:
– Data Storage: For retaining historical data.
– Data Processing and Analysis: For deriving insights from the collected data, which could include real-time analysis and long-term trends.
4. User Interface: This is the platform through which users interact with the WSN, view data, and configure settings. It could be a web application, mobile app, or desktop software.
5. Network Infrastructure: This encompasses the communication protocols and networking technologies that enable the sensor nodes to communicate with each other and with the gateway. This could involve:
– Wireless Communication Protocols: Such as Zigbee, LoRa, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth.
– Routing Protocols: For efficient data transmission across the network.
6. Security Framework: Given the potential vulnerabilities in WSNs, security measures are essential. This includes:
– Data Encryption: To protect data integrity and privacy.
– Authentication Mechanisms: To ensure that only authorized devices can access the network.
7. Energy Management: Since many sensor nodes are battery-powered, energy management strategies are critical to prolong the lifespan of the network. This may involve energy-efficient communication protocols and power-saving modes.
These components work together to create a robust wireless sensor network that can effectively monitor and respond to various environmental conditions.

COMMENTS