* Question
What is the principle of chip inductance?
* Answer
Chip inductors, also known as surface mount inductors or SMD inductors, operate on the basic principle of inductance, which is a fundamental property of electrical circuits. Here’s a breakdown of the principle and how chip inductors work:
Principle of Inductance
Inductance is the property of an electrical conductor by which a change in current flowing through it induces an electromotive force (EMF) in both the conductor itself (self-inductance) and in any nearby conductors (mutual inductance). This effect is predominantly due to two phenomena:
– Magnetic Field: When current flows through a conductor, it generates a magnetic field around it. The strength and configuration of this magnetic field depend on the current magnitude and the shape of the conductor.
– Electromagnetic Induction: According to Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, any change in the magnetic environment of a coil of wire will cause a voltage (or EMF) to be induced in the coil. This is the basic operating principle of inductors.
Construction and Operation of Chip Inductors
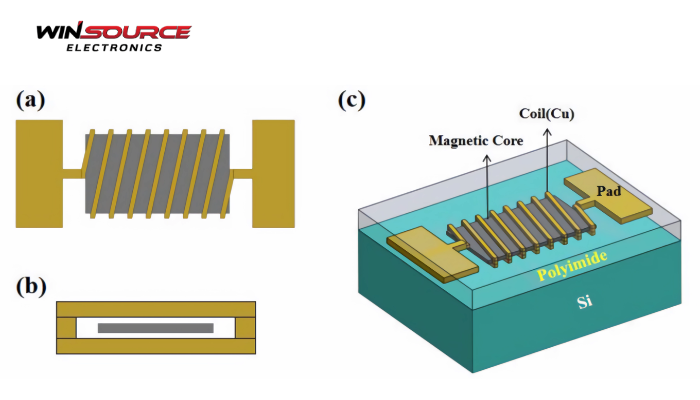
1. Core Material: Chip inductors are typically constructed with a magnetic core, which may be made from materials such as ferrite or metal alloy. The core material enhances the magnetic field created by the coil, increasing the inductor’s efficiency and inductance.
2. Coil Windings: Around the core, wire is wound to form a coil. The number of turns, the type of wire, and the core material influence the total inductance value. More turns or a core with higher permeability increases inductance.
3. Configuration: Chip inductors are designed to be compact, allowing them to be mounted directly onto printed circuit boards (PCBs) in surface mount technology (SMT) applications. They are available in various sizes and shapes to suit different circuit requirements.
Functional Role in Circuits
– Energy Storage: Chip inductors store energy in the form of a magnetic field when current flows through them. This energy is released when the current flow decreases.
– Filtering: They are used in electronic circuits to filter out unwanted frequencies. For example, in power supplies, they block high-frequency noise while allowing DC or low-frequency signals to pass.
– Resonance: In combination with capacitors, inductors are used to create resonant circuits, which are fundamental in applications like RF (radio frequency) communication and tuning systems.
– Impedance Matching: They are critical in matching the impedance between different parts of a circuit to maximize energy transfer and minimize signal reflection.
Chip inductors leverage these principles to perform critical roles in modern electronic devices, from power management to signal processing. Their small size and high reliability make them suitable for densely packed electronic assemblies.

COMMENTS