* Question
Are there several types of point contact diodes classified by forward and reverse characteristics?
* Answer
Yes. Point-contact diodes can be classified into several types based on their forward conduction and reverse blocking characteristics.
This classification reflects how the diode behaves electrically under forward bias and reverse bias, which directly affects its practical applications.
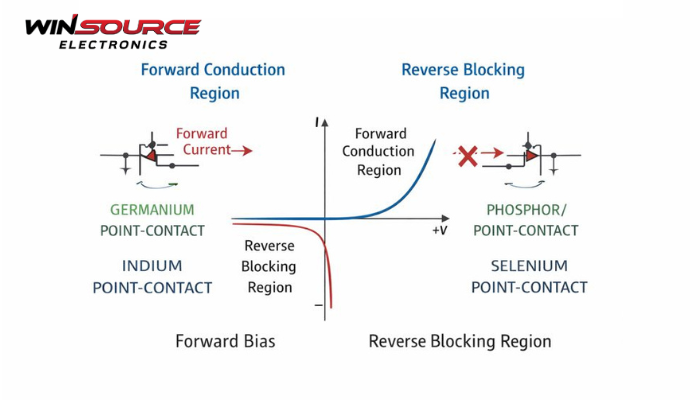
1. What Is a Point-Contact Diode (Brief Reminder)
A point-contact diode uses a very small metal-to-semiconductor contact area to form the junction.
Because of this structure, it has:
- Very small junction capacitance
- Fast response speed
- Limited power-handling capability
Point-contact diodes were widely used in early radio detection and high-frequency signal processing.
2. Classification by Forward Characteristics
2.1 Low Forward Resistance Point-Contact Diodes
These diodes exhibit:
- Low forward turn-on voltage
- Relatively large forward current for small input signals
Typical Use:
- Signal detection
- RF demodulation
They are suitable for applications where small signals need to be detected efficiently.
2.2 Nonlinear Forward Characteristic Diodes
Some point-contact diodes show:
- Strong nonlinearity in forward conduction
Typical Use:
- Mixing and detection in radio-frequency circuits
Their nonlinear behavior makes them useful in signal processing rather than power conduction.
3. Classification by Reverse Characteristics
3.1 Weak Reverse Blocking Diodes
These diodes:
- Have limited reverse voltage capability
- Allow noticeable leakage current under reverse bias
Typical Use:
- Low-voltage, high-frequency circuits
They are not suitable for high reverse-voltage applications.
3.2 Point-Contact Detector Diodes
Some point-contact diodes are designed to:
- Operate near zero bias
- Respond quickly to alternating signals
Typical Use:
- Crystal radios
- Signal detection and rectification of small RF signals
Their reverse characteristic is optimized for sensitivity rather than strong blocking.
4. Practical Meaning of This Classification
Classifying point-contact diodes by forward and reverse characteristics helps users understand:
- Whether the diode is better suited for detection, mixing, or rectification
- Its limitations in reverse voltage and power handling
- Why point-contact diodes are rarely used in modern power electronics
In modern designs, PN junction diodes and Schottky diodes have largely replaced point-contact diodes due to better stability and higher reliability.
Engineering Insight
Point-contact diodes are historically important but technically limited.
Their classification by forward and reverse characteristics highlights why they excel in high-frequency, low-power signal applications, yet perform poorly in high-voltage or high-current roles.
Conclusion
Yes, point-contact diodes can be classified into different types based on their forward conduction behavior and reverse blocking characteristics.
These differences determine whether a point-contact diode is used for signal detection, mixing, or low-power rectification, and also explain why their applications are limited compared with modern diode technologies.

COMMENTS