* Question
At Present, What Are the Commonly Used Switching Devices?
* Answer
Switching devices are electronic components used to control the on/off state of current or voltage in a circuit.
They play a fundamental role in power conversion, motor control, signal switching, and digital systems.
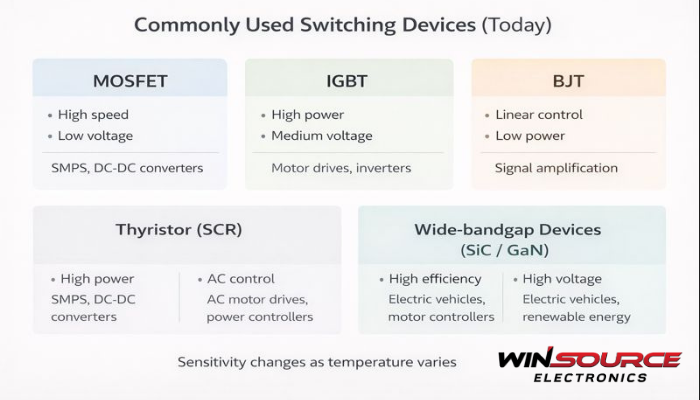
At present, the most commonly used switching devices can be grouped into the following categories.
1. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
Overview
BJTs were among the earliest widely used switching devices.
- Current-controlled devices
- Available as NPN and PNP types
Typical Applications
- Low-frequency switching
- Simple control circuits
- Legacy industrial and educational designs
Customer Note
BJTs are still used today, but they are gradually being replaced in many applications due to lower efficiency and higher drive requirements.
2. Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs)
Overview
MOSFETs are currently one of the most widely used switching devices.
- Voltage-controlled
- Fast switching speed
- Low on-resistance
Typical Applications
- Switching power supplies
- DC–DC converters
- Motor drives
- Battery-powered systems
Why They Are Popular
MOSFETs offer high efficiency, fast response, and easy gate driving, making them ideal for low- to medium-voltage applications.
3. Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs)
Overview
IGBTs combine features of MOSFETs and BJTs.
- Voltage-controlled gate
- High voltage and current capability
Typical Applications
- Inverters
- Industrial motor control
- UPS systems
- Renewable energy systems
Customer Note
IGBTs are preferred in medium- to high-power applications where MOSFET losses become excessive.
4. Thyristors (SCRs and Related Devices)
Overview
Thyristors are robust switching devices designed for high-voltage and high-current control.
Common types include:
- SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier)
- TRIAC
- GTO
Typical Applications
- AC power control
- Phase-controlled rectifiers
- Industrial heating and lighting control
Customer Note
Once turned on, many thyristors cannot be turned off by the control signal alone, which limits their use in high-frequency switching.
5. Solid-State Relays (SSR)
Overview
SSRs use semiconductor devices to perform switching without mechanical contacts.
Typical Applications
- Industrial automation
- PLC output modules
- Isolation-required control systems
Advantages
- No mechanical wear
- Silent operation
- Long service life
Engineering Insight
Different switching devices are optimized for different needs:
- MOSFETs→ high-speed, low-voltage, high-efficiency
- IGBTs→ high-power and high-voltage systems
- BJTs→ simple or legacy designs
- Thyristors→ robust AC and high-current control
- SSRs→ isolation and reliability-focused applications
Selecting the right switching device depends on voltage level, current, switching frequency, efficiency, and control method.
Conclusion
At present, the most commonly used switching devices include:
- BJTs (Bipolar Transistors)
- MOSFETs
- IGBTs
- Thyristors (SCR, TRIAC, etc.)
- Solid-State Relays
Each type serves a distinct role in modern electronic systems, and understanding their differences helps customers and engineers choose the most suitable solution for their specific applications.

COMMENTS