* Question
Optocoupler parameters
* Answer
Optocouplers (also known as optoisolators) are electronic components that provide electrical isolation between input and output circuits while allowing signal transfer via light. When designing or analyzing circuits with optocouplers, several key parameters should be considered:
1. Input Parameters
1). Forward Voltage (VF):
– The voltage required to activate the LED inside the optocoupler.
– Typical Range: 1.0 V to 1.5 V for infrared LEDs.
2). Forward Current (IF):
– The current needed to drive the LED to emit light.
– Typical Range: 5 mA to 20 mA.
3). Maximum Input Current (IF_max):
– The maximum allowable current through the LED without damage.
– Typical Range: 50 mA to 100 mA.
2. Output Parameters
1). Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE_max):
– The maximum voltage the phototransistor can withstand between collector and emitter terminals.
– Typical Range: 20 V to 80 V.
2). Collector Current (IC):
– The maximum allowable current through the phototransistor’s collector.
– Typical Range: 20 mA to 50 mA.
3). Saturation Voltage (VCE(sat)):
– The collector-emitter voltage when the phototransistor is fully “on.”
– Typical Range: 0.1 V to 0.4 V.
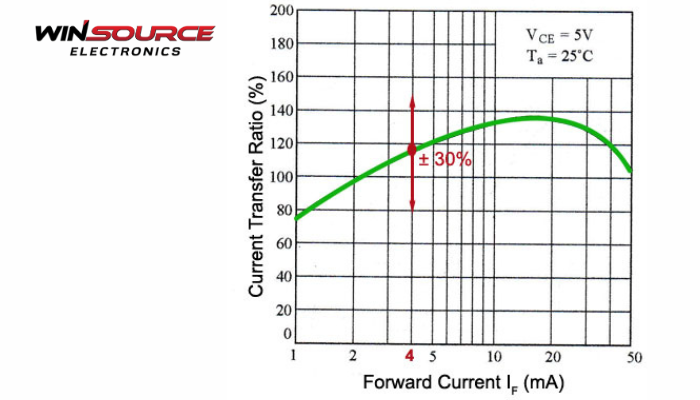
4). Output Current Transfer Ratio (CTR):
– Ratio of output current (IC) to input current (IF).
– Expressed as a percentage:CTR =IC/IF*100%.
– Typical Range: 50% to 600%, depending on the optocoupler type.
3. Isolation Parameters
1). Isolation Voltage (VISO):
– The maximum voltage the optocoupler can isolate between input and output circuits.
– Typical Range: 1 kV to 5 kV RMS.
2). Creepage Distance:
– The shortest path along the surface of the package between input and output terminals.
– Important for high-voltage applications.
3). Clearance Distance:
– The shortest path through air between input and output terminals.
4. Dynamic Parameters
1). Response Time (Rise/Fall Time):
– Time required for the optocoupler to respond to changes in input signal.
– Typical Range: 2 µs to 20 µs for standard optocouplers; faster for high-speed models.
2). Cutoff Frequency (fC):
– The maximum frequency at which the optocoupler can operate effectively.
– Typical Range: 100 kHz to several MHz (for high-speed optocouplers).
5. Environmental Parameters
1). Operating Temperature Range (TA):
– The temperature range in which the optocoupler operates reliably.
– Typical Range: -40°C to +100°C.
2). Storage Temperature Range (TS):
– The allowable temperature range for storing the optocoupler.
3). Humidity:
– The device’s ability to withstand high-humidity environments without degradation.
6. Special Parameters (for Advanced Optocouplers)
1). Noise Immunity:
– The ability to withstand electrical noise and transients without malfunction.
2). Linearity:
– Important for analog signal transmission, ensuring minimal distortion.
3). Input Capacitance (CIN):
– The parasitic capacitance of the LED.
4). Leakage Current (ICE(leak)):
– The small current flowing through the phototransistor when it is “off.”
Summary Table of Key Parameters:
Category | Parameter | Typical Range |
Input | Forward Voltage (VF) | 1.0 V to 1.5 V |
| Forward Current (IF) | 5 mA to 20 mA |
Output | Collector Voltage (VCE_max) | 20 V to 80 V |
| Current Transfer Ratio (CTR) | 50% to 600% |
Isolation | Isolation Voltage (VISO) | 1 kV to 5 kV RMS |
Dynamic | Response Time | 2 µs to 20 µs |
Environmental | Operating Temperature | -40°C to +100°C |
By understanding and considering these parameters, you can select the appropriate optocoupler for your application.

COMMENTS