* Question
What Is the Role and Operating Principle of the Cycle Control Scheme?
* Answer
A cycle control scheme is a control method used to regulate system behavior by adjusting the operating cycle or duty cycle of a device or signal.
It is commonly applied in power electronics, motor control, heating control, and digital systems, where precise control of energy, speed, or output level is required.
In simple terms, cycle control determines how long a device stays ON and OFF within each operating cycle.
1. Role of the Cycle Control Scheme
The main roles of a cycle control scheme include:
1.1 Output Regulation
By adjusting the duty cycle, the system can control:
- Output voltage or current
- Motor speed or torque
- Heating power or brightness
This allows the system to deliver exactly the required output level.
1.2 Energy Efficiency Improvement
Cycle control helps reduce unnecessary power consumption by:
- Limiting ON time when full power is not needed
- Matching energy delivery to actual load demand
This improves overall system efficiency and reduces heat generation.
1.3 System Stability and Protection
Proper cycle control:
- Prevents overload conditions
- Avoids excessive current or voltage
- Protects components from thermal stress
It contributes to stable and reliable operation.
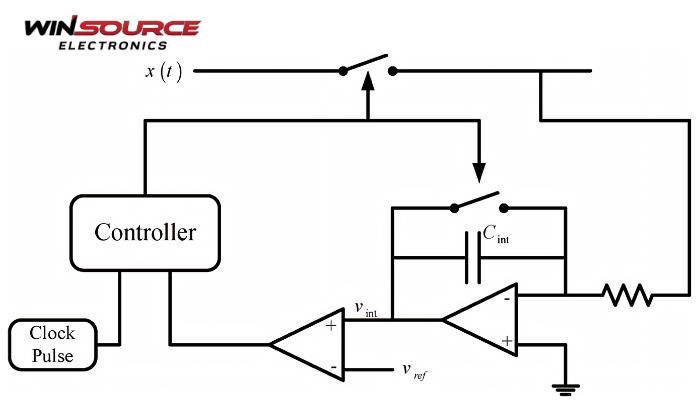
2. How the Cycle Control Scheme Works
2.1 Basic Operating Principle
Each operating cycle is divided into:
- An ON period
- An OFF period
The ratio between these two periods is called the duty cycle.
For example:
- 50% duty cycle → ON and OFF times are equal
- 75% duty cycle → ON time is longer than OFF time
Changing the duty cycle changes the system output.
2.2 Control Signal Generation
The control scheme typically:
- Compares a feedback signal (voltage, current, speed, temperature) with a reference value
- Generates a control signal based on the difference
- Adjusts the duty cycle accordingly
This process is often implemented using:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
- Digital timers or controllers
- Microcontrollers or control ICs
2.3 Closed-Loop Operation
In many systems, cycle control works in a closed-loop manner:
- Measure system output
- Compare it with the target value
- Adjust the duty cycle
- Repeat continuously
This ensures accurate and adaptive control under changing conditions.
3. Typical Application Examples
Cycle control schemes are widely used in:
- Switching power supplies (voltage regulation)
- Motor drives (speed control)
- LED dimming systems
- Temperature and heating control
- Battery charging systems
In all these cases, the scheme controls power delivery by time-based regulation rather than continuous analog adjustment.
Engineering Insight
Cycle control schemes offer a good balance between:
- Control accuracy
- Implementation simplicity
- High efficiency
Because switching devices operate mainly in ON or OFF states, losses are reduced compared with linear control methods.
Conclusion
The role of a cycle control scheme is to regulate system output, improve efficiency, and maintain stable operation by controlling the ON/OFF timing within each operating cycle.
Its operation is based on adjusting the duty cycle according to feedback, making it a fundamental and widely used control method in modern electronic systems.

COMMENTS