* Question
What is the ALOHA algorithm?
* Answer
The ALOHA algorithm is a random access protocol used to manage how multiple users share a common communication channel, especially in wireless or satellite networks. It is one of the earliest and simplest medium access control (MAC) methods, and it laid the groundwork for many modern networking technologies such as Ethernet and Wi-Fi.
1. Concept and Working Principle
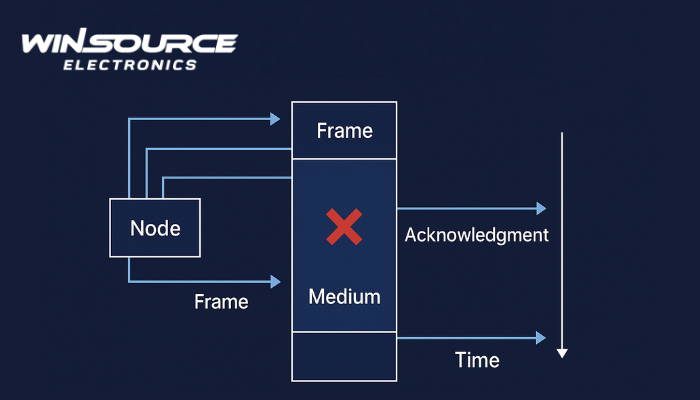
The main idea of the ALOHA algorithm is straightforward:
Each user transmits data whenever it has something to send. If two or more users transmit at the same time, a collision occurs and all those packets are destroyed. Each sender then waits a random amount of time before retransmitting, to reduce the likelihood of another collision.
This approach allows completely decentralized communication — no master controller decides who can speak when.
2. Types of ALOHA Algorithms
There are two main versions of the ALOHA algorithm, which differ in how they handle time synchronization and transmission timing:
(a) Pure ALOHA
Transmission rule: Send immediately when ready.
Collision period: Any overlap between packets causes a loss.
Efficiency: Theoretical maximum throughput is about 18.4% (≈ 1/2e).
Synchronization: Not required.
Vulnerable period: 2 × frame time.
(b) Slotted ALOHA
Transmission rule: Time is divided into equal time slots; transmissions are allowed only at the beginning of a slot.
Collision period: Only packets starting in the same slot can collide.
Efficiency: Theoretical maximum throughput is about 36.8% (≈ 1/e).
Synchronization: Required among users.
Vulnerable period: 1 × frame time.
3. Efficiency Comparison
Algorithm Type | Synchronization Needed | Vulnerable Time | Max Throughput |
Pure ALOHA | No | 2 × frame time | 18.4% |
Slotted ALOHA | Yes | 1 × frame time | 36.8% |
Slotted ALOHA roughly doubles the efficiency of Pure ALOHA by aligning transmissions to time slots and therefore reducing the probability of collision.
4. Legacy and Modern Relevance
Although the ALOHA algorithm itself is not widely used in its pure form today, its random-access and retransmission principles inspired many later network technologies, including:
CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access) – used in Ethernet.
CSMA/CD (Collision Detection) – for wired networks.
CSMA/CA (Collision Avoidance) – for Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11).
ALOHA also remains relevant in:
Satellite communication systems
Low-power IoT networks (like LoRaWAN)
RFID tag communication
5. Summary
The ALOHA algorithm was revolutionary for introducing the concept of distributed, contention-based communication, where users share a common medium without central control.
Despite its simplicity and limited efficiency, it represents a cornerstone in the evolution of data communication protocols and remains a foundation for modern wireless access methods.

COMMENTS