* Question
What are the basic elements of the simplest electromagnetic interference (EMI) model?
* Answer
The simplest EMI model breaks interference down into three fundamental elements. This structure is widely used in EMC engineering to analyze, predict, and mitigate unwanted electromagnetic disturbances.
1. Interference Source
This is the device or circuit that generates unwanted electromagnetic energy.
Sources can be intentional (e.g., switching converters, oscillators) or unintentional (e.g., motor commutation, fast digital edges).
Its key attributes include:
- Amplitude
- Frequency content
- Rise/fall time
- Spectral distribution
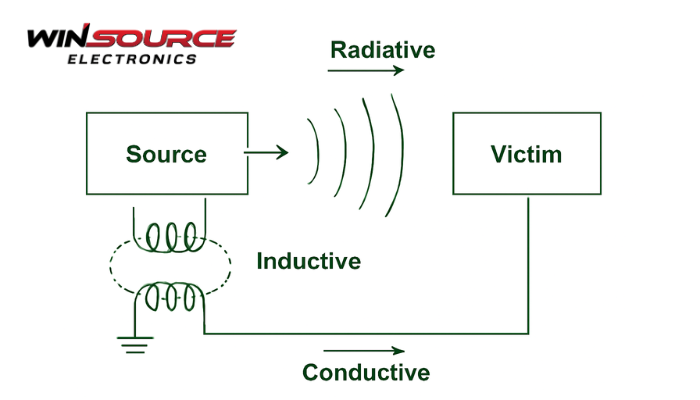
2. Coupling Path (Propagation Path)
This is the route through which interference travels from the source to the victim.
It can be:
- Conducted(through wires, ground, power rails)
- Radiated(through electromagnetic fields)
- Capacitive(electric-field coupling)
- Inductive(magnetic-field coupling)
The coupling path determines how strongly the interference reaches the affected circuit.
3. Victim (Receptor) Device
The victim is the component or system susceptible to the interference.
Its sensitivity depends on:
- Input impedance
- Operating frequency
- Shielding and filtering
- Circuit layout and grounding
If the victim’s immunity is lower than the interference level, malfunction or noise appears.
Summary
The simplest EMI model consists of:
- Source– where the unwanted energy originates
- Coupling path– how the energy propagates
- Victim– what receives and reacts to the disturbance
This three-element model supports targeted EMC design by identifying where to apply shielding, filtering, grounding improvements, or design modifications.

COMMENTS