* Question
What are the key properties of circularly polarized waves in electromagnetic systems?
* Answer
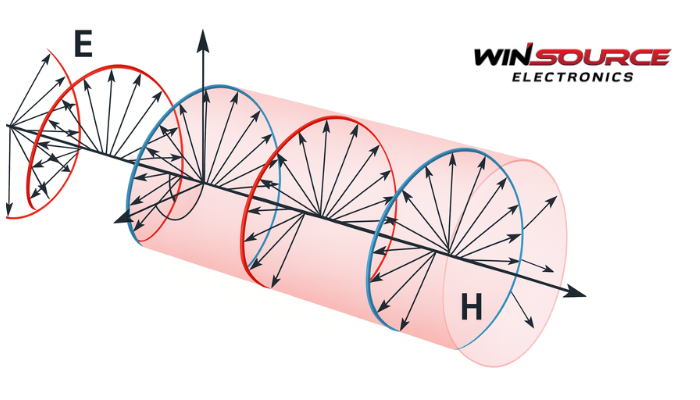
Circularly polarized waves are a special form of electromagnetic waves where the electric field vector rotates in a circular motion as the wave propagates. They are widely used in antennas, satellite communications, and optical systems. The important properties include:
1. Electric Field Rotation
The electric field maintains a constant magnitude but its direction rotates at the wave frequency.
The tip of the electric field vector traces a circle in the plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation.
2. Right-Hand and Left-Hand Polarization
Right-Hand Circular Polarization (RHCP): The electric field rotates clockwise as viewed in the direction of propagation.
Left-Hand Circular Polarization (LHCP): The electric field rotates counterclockwise.
These two polarizations are orthogonal and can be used to separate signals.
3. Constant Power Distribution
Unlike linearly polarized waves, circular polarization provides uniform power distribution in all directions perpendicular to propagation.
This reduces signal fading due to misalignment between transmitting and receiving antennas.
4. Polarization Matching
Efficient communication requires the transmitter and receiver to use the same polarization (RHCP with RHCP, LHCP with LHCP).
Cross-polarized systems (RHCP vs. LHCP) experience strong signal attenuation, which can be useful for isolation in multi-channel systems.
5. Applications
Satellite and space communications (resistant to rotation of receiving antennas).
GPS systems (commonly use RHCP).
Optical devices such as polarizers and wave plates.
Summary
The important properties of circularly polarized waves include their rotating electric field, right-hand/left-hand polarization states, constant power distribution, and polarization matching requirements. These characteristics make them highly valuable in wireless communications, satellite links, and optical systems.

COMMENTS