* Question
What is AC (alternating current)?
* Answer
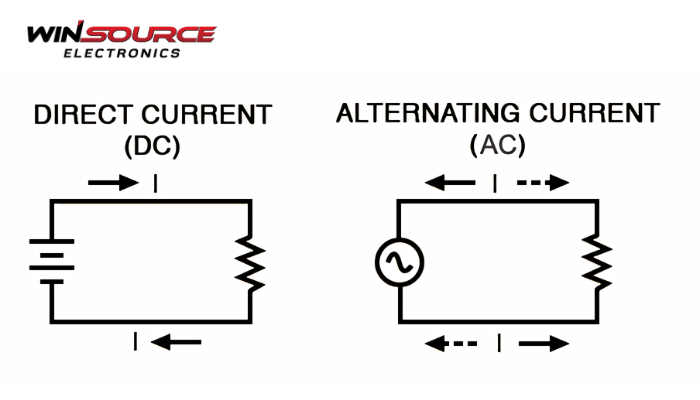
AC, or alternating current, refers to an electrical current in which the flow of electrons periodically reverses direction. Unlike direct current (DC), which moves in a single, constant direction, AC continuously alternates its polarity in a sinusoidal, square, or triangular waveform depending on the application. This alternating behavior allows electrical energy to be transmitted efficiently over long distances with minimal loss, which is why AC forms the foundation of modern power distribution systems around the world.
In most regions, AC power in homes and industries operates at standardized frequencies—typically 50 Hz or 60 Hz—meaning the current changes direction 50 or 60 times per second. The voltage level can be easily transformed using transformers, enabling high-voltage transmission for long-distance efficiency and lower-voltage distribution for safe consumer use. AC is also commonly used to power motors, HVAC systems, lighting, and industrial equipment due to its ability to generate rotating magnetic fields, which drive the operation of many electrical machines.
Whether used in national power grids, household appliances, or industrial automation, AC remains the dominant form of electrical energy delivery because of its efficiency, flexibility, and compatibility with a wide range of electrical devices.

COMMENTS