* Question
What is an optical encoder sensor?
* Answer
An optical encoder sensor is an electromechanical device used to convert the angular position, rotation speed, or linear displacement of a shaft or object into precise electrical signals. It is a fundamental component in motion control, robotics, industrial automation, and servo motor systems, providing accurate position and feedback data to control systems.
1. Working Principle
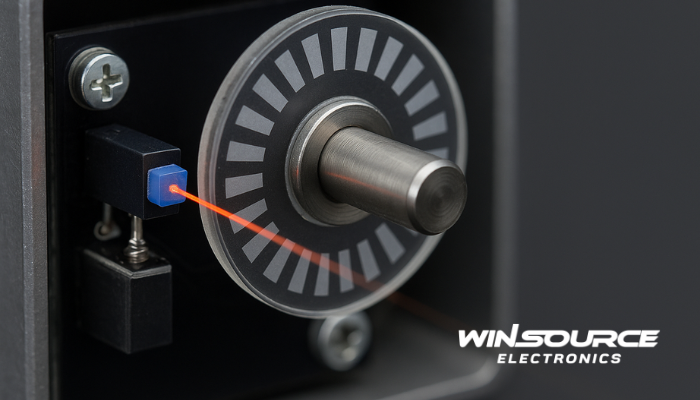
An optical encoder operates based on light interruption or reflection.
It typically consists of three main elements:
Light source: Usually an infrared LED that emits a constant beam.
Code disc or strip: A transparent disc with alternating opaque and transparent patterns.
Photo detector array: Detects the light that passes through or reflects from the code pattern.
As the shaft rotates, the light passing through the patterned disc is periodically interrupted. The detector converts these light variations into digital pulses, which are then processed to determine position, direction, and speed.
2. Types of Optical Encoders
Optical encoders can be categorized into two main types:
Incremental Optical Encoders:
Generate a series of pulses corresponding to shaft movement. The system counts these pulses to calculate relative position and speed. They are simple, cost-effective, and widely used in motion control applications.
Absolute Optical Encoders:
Provide a unique digital code for each shaft position. Even after power loss, the absolute position can be retained. These encoders are preferred in high-precision systems such as CNC machines, robotic arms, and medical imaging equipment.
3. Advantages of Optical Encoders
High resolution and precision: Capable of detecting extremely small angular changes.
Fast response: Ideal for high-speed rotational systems.
Non-contact sensing: Reduces mechanical wear and extends lifespan.
Compatibility: Can easily interface with microcontrollers, PLCs, and motion control units.
4. Typical Applications
Optical encoder sensors are widely used in:
Servo motor feedback systems
Robotics and automation lines
Position tracking in CNC and 3D printers
Aerospace and instrumentation control
Medical devices and diagnostic equipment
Conclusion
In essence, an optical encoder sensor translates mechanical motion into precise digital information, forming the backbone of many closed-loop control systems. Its ability to provide high-resolution feedback makes it indispensable in modern automation and motion control engineering.

COMMENTS