* Question
What is an Electron Capture Detector (ECD) in gas chromatography?
* Answer
An Electron Capture Detector (ECD) is a highly sensitive detection device used in gas chromatography (GC) to identify and quantify electronegative compounds, such as halogens, organometallics, nitriles, and pesticides.
It operates by measuring the reduction in electron current caused when these compounds capture free electrons generated within the detector cell.
1. Working Principle
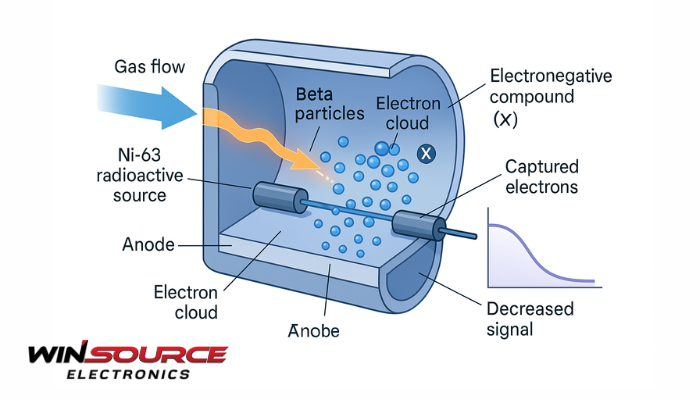
The ECD operates based on the electron capture phenomenon.
Inside the detector, a radioactive source—commonly nickel-63 (⁶³Ni)—emits beta particles (electrons) that ionize the carrier gas (often nitrogen or argon–methane).
This ionization produces a steady flow of free electrons, creating a baseline current between the anode and cathode.
When an analyte containing electronegative atoms (such as chlorine, fluorine, or oxygen) enters the detector:
- These molecules capturesome of the free electrons.
- The number of electrons reaching the anode decreases, reducing the measured current.
- The detector converts this change into a signal proportional to the analyte concentration.
2. Key Characteristics
- Extremely high sensitivity:Detects compounds at concentrations as low as femtograms (10⁻¹⁵ g).
- Selective response:Especially sensitive to halogenated and electron-withdrawing molecules.
- Non-destructive detection:The sample is not consumed, allowing further analysis if needed.
- Stable and reproducible signal:Provides consistent results over a wide range of conditions.
3. Applications
The ECD is widely used in:
- Environmental analysis:Detection of halogenated hydrocarbons, PCBs, and pesticide residues.
- Pharmaceutical testing:Monitoring trace impurities or degradation products.
- Forensic and toxicology studies:Identifying organohalogen compounds.
- Industrial safety monitoring:Tracing chlorinated solvents and refrigerants.
4. Advantages and Limitations
Advantages | Limitations |
Very high sensitivity (10⁻¹² to 10⁻¹⁵ g range) | Limited to electronegative analytes |
Stable, low-noise baseline | Requires radioactive source handling |
Non-destructive detection | Sensitive to contamination and carrier gas purity |
Excellent for trace analysis | Slower response time compared to FID or TCD |
Summary Insight
In summary, the Electron Capture Detector (ECD) is a specialized and ultra-sensitive detector that leverages the principle of electron attachment to identify trace-level electronegative compounds in gas chromatography.
It remains an indispensable tool in environmental monitoring, pesticide detection, and halogenated compound analysis, valued for its selectivity, precision, and unparalleled sensitivity.

COMMENTS