* Question
What is the inverse piezoelectric effect?
* Answer
The inverse piezoelectric effect is a fundamental principle in materials science and electromechanics. Here’s a comprehensive explanation:
Table of Contents
ToggleDefinition:
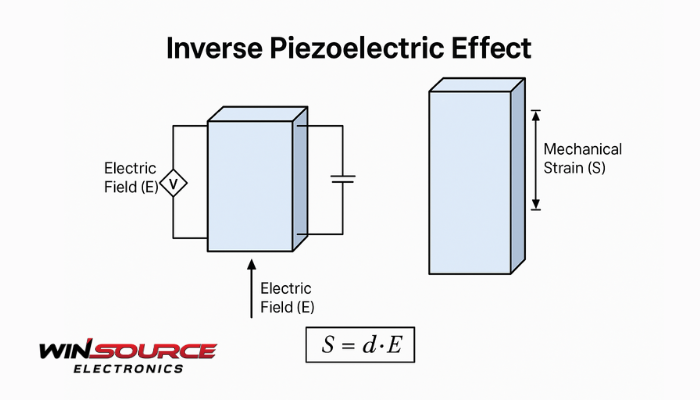
The inverse piezoelectric effect refers to the phenomenon in which an applied electric field causes certain piezoelectric materials to deform mechanically—that is, they change their shape or dimensions.
How It Works:
Piezoelectric materials (such as quartz, PZT, or PVDF) have a crystal structure that lacks a center of symmetry.
When an electric voltage is applied across the material:
The internal dipole moments reorient, leading to a mechanical strain (expansion or contraction).
This deformation is reversible and proportional to the strength and polarity of the applied field.
Relation to the Piezoelectric Effect:
The direct piezoelectric effect: Mechanical stress → generates electric charge.
The inverse piezoelectric effect: Electric field → induces mechanical deformation.
Both effects are described by the same material constants (piezoelectric coefficients, usually denoted as d, g, or e constants).
Mathematical Expression:
The inverse piezoelectric effect can be expressed as:
S=d⋅E
Where:
S = mechanical strain (dimensionless)
d = piezoelectric strain coefficient (m/V or C/N)
E = applied electric field (V/m)
Applications:
The inverse piezoelectric effect is used in devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical movement, such as:
Inkjet printer heads (piezoelectric actuation to eject droplets)
Ultrasonic transducers
Micro-positioning stages and actuators
Piezo buzzers and speakers
Adaptive optics and precision control systems
Summary Table
Aspect | Description |
Effect Type | Inverse piezoelectric effect |
Cause | Application of an electric field |
Result | Mechanical deformation (strain) |
Materials | Quartz, PZT, PVDF, BaTiO₃, etc. |
Key Applications | Inkjet printers, medical ultrasound, actuators, sensors |

COMMENTS