* Question
What Is the Priority-Based Cache Management Strategy?
* Answer
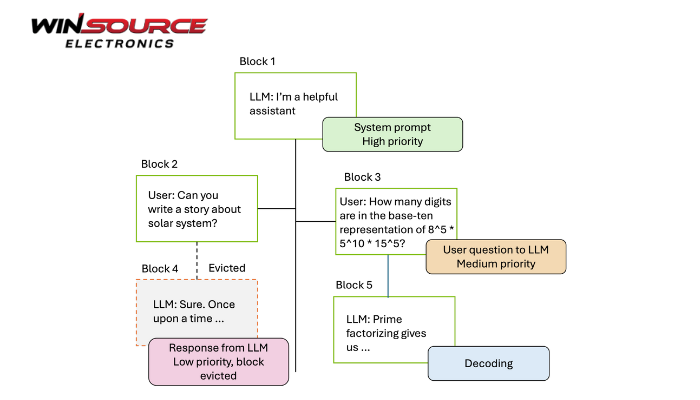
A priority-based cache management strategy is a cache control approach in which cached data is assigned different priority levels, and cache allocation, retention, or eviction decisions are made based on those priorities.
Its main objective is to ensure that high-value or time-critical data remains in cache, even under limited cache capacity.
This strategy is widely used in operating systems, CPUs, databases, storage controllers, and network systems.
1. Core Idea of Priority-Based Cache Management
Unlike traditional cache strategies that treat all cached data equally, a priority-based approach:
- Assigns priority attributesto cache entries
- Retains high-priority data longer
- Evicts low-priority data first when cache space is needed
In essence, not all cache entries are equal, and importance directly influences cache behavior.
2. How Priority Is Typically Determined
Priority can be assigned using different criteria depending on the system design:
2.1 Access Frequency
Data accessed more frequently may be given higher priority.
2.2 Access Recency
Recently accessed data may temporarily receive elevated priority.
2.3 Application or Process Importance
Caches may prioritize:
- Real-time tasks
- Kernel data
- Critical services
2.4 Data Type or Function
Examples include:
- Instruction cache vs. data cache
- Metadata vs. bulk data
- Control information vs. payload
3. Cache Replacement Behavior
When the cache reaches capacity, the strategy determines which entries to evict:
- High-priority entriesare protected from eviction
- Low-priority entriesare removed first
- Eviction may still consider secondary rules such as LRU or LFU within the same priority class
This often results in a hybrid strategy, such as:
- Priority + LRU
- Priority + LFU
4. Typical Application Scenarios
4.1 CPU Cache Systems
Critical instruction paths or frequently used data structures may be given higher cache priority to reduce latency.
4.2 Operating Systems
Kernel memory pages often have higher priority than user-space pages in page cache management.
4.3 Database Systems
Indexes and metadata may be prioritized over raw table data to improve query performance.
4.4 Network and Storage Systems
- Control packets are prioritized over bulk data
- Hot blocks in SSD caches are retained longer
5. Advantages and Trade-Offs
Advantages
- Improves performance for critical workloads
- Reduces cache pollution from low-value data
- Enhances system predictability
Trade-Offs
- Increased management complexity
- Requires accurate priority assignment
- Poor priority tuning can reduce cache efficiency
Engineering Insight
Priority-based cache management is especially valuable in mixed-workload systems, where latency-sensitive tasks coexist with throughput-oriented workloads.
Modern systems often combine priority-based logic with adaptive algorithms to dynamically adjust priorities based on runtime behavior.
In practice, priority-based strategies are rarely standalone—they are usually layered on top of classical cache algorithms to balance fairness and performance.
Conclusion
A priority-based cache management strategy controls cache allocation and eviction by assigning importance levels to cached data.
By ensuring that high-priority data remains in cache while less important data is evicted first, this approach improves performance, responsiveness, and reliability in complex computing systems.

COMMENTS