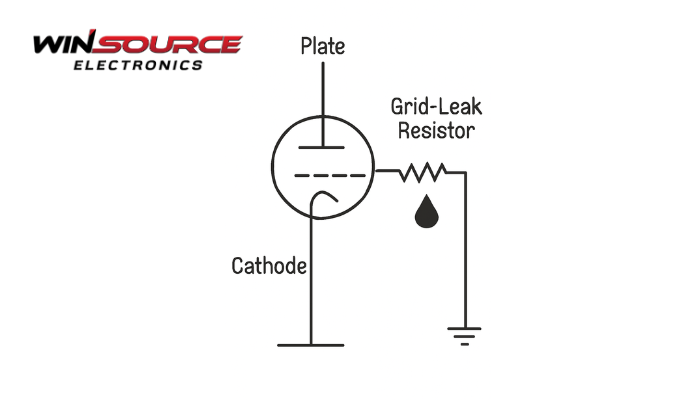
* Question
What is the role of the grid (grid-leak) resistor in a triode?
* Answer
The grid—or grid-leak—resistor in a vacuum-tube triode is an essential biasing and stabilization component. It performs several key functions related to setting the operating point, ensuring stability, and forming the input impedance of the stage.
1. Provides the Required Negative Grid Bias
In most triode amplifier circuits, the grid must be negative relative to the cathode.
The grid resistor:
- Connects the grid to ground (or a bias source)
- Ensures the grid stays at the required DC bias voltage
- Prevents the grid from floating
This establishes a stable operating point for linear amplification.
2. Creates the “Grid-Leak Bias” Path
During operation, some electrons strike the grid and accumulate charge.
The grid-leak resistor:
- Provides a discharge path for these electrons
- Prevents the grid from becoming positive
- Helps maintain correct negative bias automatically
This is the classic “grid-leak bias” mechanism used in many triode stages.
3. Limits Grid Current and Protects the Tube
If the input signal drives the grid momentarily positive:
- The grid will draw current
- The grid-leak resistor limits this current
- Protects the grid from overheating or distortion
Thus, it also functions as a protective element.
4. Defines the Input Impedance of the Triode Stage
The resistor is usually large (100 kΩ – several MΩ), and it largely determines:
- The input impedance seen by the previous stage
- The loading effect on the signal source
- The AC coupling characteristics
A large grid resistor allows a high-impedance, minimally loaded input.
5. Improves Stability and Reduces Oscillation
By providing a resistive reference for the grid, the grid-leak resistor:
- Suppresses unwanted oscillations
- Reduces RF feedback and parasitics
- Improves amplifier stability
This is especially important in high-gain or RF triodes.
Summary
The grid (grid-leak) resistor in a triode:
- Provides the required negative grid bias
- Discharges accumulated grid electrons
- Limits grid current during positive swings
- Sets the input impedance
- Improves circuit stability
These functions ensure the triode operates linearly, safely, and predictably.

COMMENTS