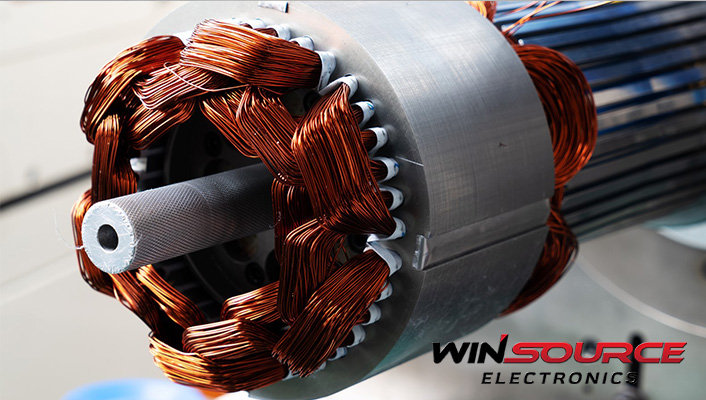
AC motors are quintessential elements in today’s mechanized landscape. They adeptly transform electrical energy into mechanical force, energizing many devices. These motors are now integral to contemporary life, being the driving force behind common appliances like fans and pumps and fueling massive industrial machinery.
The journey of the AC motor is one of evolution and innovation. Central to its progression is the monumental work of Nikola Tesla. This visionary inventor laid the foundational blueprint for the modern AC motor we recognize today. Through persistent refinements and adaptations, driven by the expertise of leading electronic providers, AC motors continue to be at the forefront of technological advancement.
Table of Contents
ToggleBasic Principles of AC Motors
At the heart of the AC motor lies Alternating Current (AC), a type of electric current where the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction. When this alternating current passes through coils within the motor, it produces a changing magnetic field. This dynamic interplay between electricity and magnetism is crucial, as the interaction between the magnetic fields and the electrical current creates a rotational force, making the motor turn.
Types of AC Motors
Synchronous Motors
Distinguished by their ability to operate at a constant speed irrespective of the load, synchronous motors rely on electricity and magnetism to generate motion. Their dependable nature makes them suitable for precision applications like clocks and certain machinery types.
Permanent Magnet AC (PMAC) Motors
Permanent Magnet AC (PMAC) Motors, as their name implies, are characterized by including permanent magnets on the rotor. Combined with the traditional stator windings, these magnets produce a magnetic field. When this field from the permanent magnets interacts with the stator’s field, it induces rotation.
One of the significant strengths of PMAC motors is their efficiency in transmuting electrical energy into mechanical power. This high efficiency makes them a preferred choice across a spectrum of applications. They are extensively employed in sectors ranging from automotive to varied industrial processes, especially when conserving energy is a key concern.
Asynchronous (Induction) Motors
These motors derive their name because their rotor rotates at a speed different from the stator’s magnetic field. Induction motors cater to various applications with variations like split-phase and capacitor start designs. Their efficiency and rugged design have led to widespread use in everything from household appliances to industrial equipment.
Wound Rotor (or Slip Ring) Motors
Wound Rotor or Slip Ring Motors are distinguished by their rotor design. The rotor in these motors is equipped with windings that connect to an external circuit via slip rings. This design bestows them with a distinct advantage: the capacity to modulate the motor’s speed and torque characteristics. Such a feature becomes invaluable in scenarios demanding a robust starting torque.
Consequently, these motors are common in industrial environments and crucial in machineries like elevators and hoists.
Components of AC Motors
● A deeper look into the AC motor reveals a series of vital components, each playing a unique role:
● The stator, stationary coils, plays a pivotal role by producing the magnetic field when AC flows through it.
● Rotors come in distinct designs: the squirrel cage, known for its durability, and the wound rotor, recognized for its adaptability in controlling speed.
Additional components, such as bearings, ensure the motor’s smooth operation, while the shaft is central to transmitting the generated mechanical energy. External connectors also play a vital role, providing the necessary connections for power and control functions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AC Motors
With every piece of technology, there are strengths and challenges to consider:
Pros:
● AC motors stand out due to their uncomplicated designs, making them easy to manufacture and use.
● Their durability ensures a prolonged operational life with relatively low maintenance needs.
● An added benefit is their adaptability; they can function efficiently with various power sources and speeds.
Cons:
● One of the setbacks is the potential for power loss, especially when operating under fluctuating loads.
● Starting an AC motor requires certain considerations, as improper startup methods can lead to wear and tear.
Understanding AC motors’ core principles, history, types, and intricacies provides insight into their significant role in modern industry and technology. As they continue to evolve, they promise to remain instrumental in powering the world around us.
AC Motor Control and Drives
The precision in tasks that AC motors perform underscores the necessity of effective control over their speed and direction. In dynamic industrial settings, for instance, a slight variation in motor speed can make the difference between a product’s quality assurance and its rejection.
Enter Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), sophisticated devices designed to regulate the speed and torque of an AC motor. VFDs offer unparalleled control by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor.
One notable benefit of integrating VFDs with AC motors is energy conservation, as motors can operate only at the needed speed, reducing energy wastage. Moreover, VFDs grant smoother operational control, thus extending the motor’s lifespan and decreasing wear and tear.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Like any machinery, AC motors are not exempt from occasional malfunctions. Overheating, excessive vibration, and unusual noises rank among the more prevalent issues. A proactive approach to maintenance can alleviate most of these concerns.
Lubricating moving parts, ensuring secure connections and regular cleaning can remarkably extend the life of an AC motor. While routine inspections can identify and rectify minor problems, there is a pronounced importance in seeking professional maintenance services to diagnose deeper issues and ensure optimal functionality.
Environmental and Energy Efficiency Considerations
Energy efficiency is more than a catchphrase; it’s a critical criterion for modern machinery. AC motors come with efficiency ratings that provide insights into their energy consumption patterns, guiding users toward making informed decisions. These motors undeniably contribute to energy conservation efforts by optimizing energy use and reducing industrial carbon footprints.
Environmentally, the push towards greener and more sustainable practices has influenced motor designs, leading to the development of motors that consume less power and generate minimal waste. Manufacturers are now more conscious of using environmentally friendly materials and processes.
Future Trends in AC Motor Technology
AC motors are poised for groundbreaking advancements in the tapestry of technological evolution. We foresee smart technology playing a transformative role. With the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), motors can be remotely monitored and controlled, making predictive maintenance—a technique to predict when equipment will fail—a reality.
Additionally, AC motors equipped with artificial intelligence capabilities can be anticipated as automation continues its upward trajectory in various sectors. Such advancements are not mere novelties but are geared toward optimizing efficiency, reliability, and adaptability.
As the horizon of the future unfolds, AC motors are bound to remain at the forefront, driving innovations while adhering to sustainable practices, ensuring they remain integral in a world constantly in motion.

COMMENTS