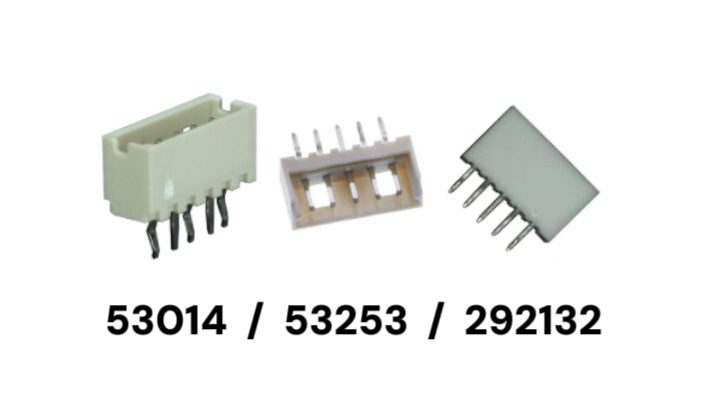
In industrial control systems, embedded platforms, and compact power distribution designs, 2.0mm pitch wire-to-board connectors are widely used for signal routing and low-current power delivery. While these components may look interchangeable on a datasheet, their real-world differences become evident at the system level—particularly in assembly robustness, vibration performance, and long-term serviceability.
This guide compares three commonly used 2.0mm, 5-pin, vertical, through-hole (THT) connectors: Molex 53014-0510, Molex 53253-0570, and TE Connectivity 292132-5. Although they share similar electrical ratings, each reflects a distinct design focus. We evaluate them across locking mechanisms, assembly reliability, and wire-harness ecosystems, helping engineers avoid solutions that are electrically compatible yet mechanically risky.
Parameter Comparison
53014-0510 | 53253-0570 | 292132-5 | |
Series | MicroBlade™ | Micro-Latch™ | AMP CT |
Locking method (vibration / retention) | Friction lock | Latch | Latch |
Rated current / voltage | Max 2.0A / 125V | Max 2.0A / 125V | Max 2.0A / 125V |
Mating feedback | Soft, minimal tactile feedback | Clear “click” engagement | Clear “click” engagement |
Vibration resistance | Medium | High | High |
PCB footprint constraint | Compact | Requires latch-side keepout for operation | Requires latch-side keepout for operation |
Key selection note | Extra harness securing recommended under vibration/tension | Must reserve keepout for maintenance access | Cross-brand migration requires footprint + terminal ecosystem validation |
Application Analysis
- 53014-0510
Best for: Internal wiring in consumer electronics, space-constrained instrumentation, and modules that are rarely unplugged or serviced.
Insight: Uses a friction-fit retention design, offering a compact footprint and fast assembly in static applications. Without a positive latch, it is more likely to loosen under sustained cable tension or vibration. Not recommended for dynamic wiring such as motor leads, moving harnesses, or drag-chain applications.
- 53253-0570
Best for: Industrial automation controllers, servo/motion-control I/O, robotics, and sensor aggregation in vibration-prone environments.
Insight: The positive latch provides clear tactile/audible engagement, helping reduce partial insertion and incomplete mating on the production line. With higher retention force and stronger vibration resistance, it is well suited for systems requiring long-term connection stability and field serviceability.
- 292132-5
Best for: Energy storage systems (BMS), security/access control products, and globally standardized hardware platforms.
Insight: AMP CT is widely adopted as a mature connector ecosystem, offering broad availability of wire-side housings and terminals—including IDC options for high-throughput harness production. It also features a robust locking mechanism comparable to Micro-Latch, and is a strong fit for platform-level designs where second sourcing, standardized tooling, and multi-site manufacturing consistency matter.
Design Considerations
- Locking trade-off
Friction lock (53014): Compact and simple—best for static, enclosed connections. In high vibration or cable-tension conditions, add strain relief (e.g., cable ties/clamps/adhesive).
Positive latch (53253 / 292132): Preferred for reliability. PCB note: leave a latch-side keepout area so technicians can release the latch; otherwise servicing becomes difficult or impossible.
- Harness ecosystem trap
No cross-compatibility: Housings and crimp terminals across these series are not interchangeable.
Tooling impact: Switching families typically requires new crimp dies/applicators at the harness supplier.
Process tolerance: MicroBlade terminals have a tighter crimp window; Micro-Latch and AMP CT are generally more robust for mass production.
Replacement and Migration Guidance
- 53014 → 53253
Migration notes: Not a drop-in replacement. Requires PCB layout changes (footprint + keepout) and a complete harness change. Only recommended when upgrading from light-duty internal wiring to industrial-duty applications.
- 53253 ↔ 292132
Migration notes: Functional equivalent, but mechanically distinct. If you need a second source, validate both early. Consider a dual-layout footprint or compatible solder pads, and prepare separate harness drawings.
- 53014 → 292132
Migration notes: Complete redesign required. Mechanical and electrical ecosystems are different. Best addressed during the concept phase (Parallel Design) rather than mid-production.
Key Takeaways
- 53014: Light-duty internal wiring
- 53253: Industrial vibration-resistant applications
- 292132: Harness Standardization / strong second-source candidate
WIN SOURCE provides stable supply and technical support for leading connector brands such as Molex and TE Connectivity. From selection confirmation to alternative qualification, we help customers reduce supply chain risk and improve mass-production readiness. Visit WIN SOURCE to check real-time inventory and pricing.
©2026 Win Source Electronics. All rights reserved. This content is protected by copyright and may not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, cached or otherwise used, except with the prior written permission of Win Source Electronics.

COMMENTS