* Question
What Pipeline Conflicts Can Occur in the C28x (28x) DSP Architecture?
* Answer
In the TMS320C28x (28x) DSP architecture from Texas Instruments, a pipeline conflict occurs when instructions cannot flow smoothly through the CPU pipeline due to data dependencies, resource contention, or control flow changes.
These conflicts may cause pipeline stalls, reducing execution efficiency.
Understanding these conflicts helps users optimize code performance, especially in real-time control and motor-drive applications where C28x devices are widely used.
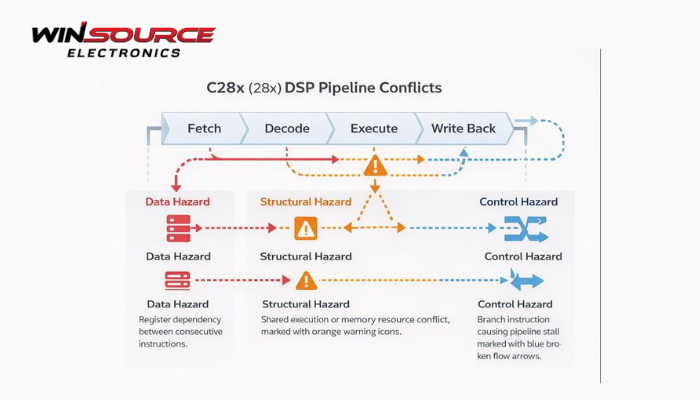
1. Data Hazards (Data Dependency Conflicts)
What It Is
A data hazard occurs when an instruction depends on the result of a previous instruction that has not yet completed its execution in the pipeline.
Typical Scenario
- One instruction writes to a register
- The next instruction immediately tries to read that same register
Because the data is not yet available, the pipeline may insert a stall cycle.
Impact
- Increased instruction latency
- Reduced execution efficiency
2. Resource Conflicts (Structural Hazards)
What It Is
A resource conflict happens when multiple instructions attempt to use the same hardware resource at the same time.
Typical Resources Involved
- Data memory buses
- Register files
- Arithmetic units
Since the C28x has limited shared resources, simultaneous access requests can cause one instruction to wait.
Impact
- Pipeline stalls
- Lower instruction throughput
3. Program Flow Conflicts (Control Hazards)
What It Is
A program flow conflict occurs when the execution path changes unexpectedly, such as with:
- Conditional branches
- Jumps
- Interrupts
Because the pipeline has already fetched upcoming instructions, a control change may invalidate them.
How C28x Handles This
- Prefetched instructions may be discarded
- The pipeline is flushed and refilled
Impact
- Additional execution cycles
- Reduced efficiency in branch-heavy code
4. Memory Access Conflicts
What It Is
Memory access conflicts occur when instructions compete for program memory or data memory access in the same cycle.
Typical Example
- An instruction fetch
- A simultaneous data read or write
If both access the same memory interface, the pipeline may stall.
Engineering Insight
Pipeline conflicts do not cause incorrect results, but they directly affect execution speed.
In C28x DSP applications—such as motor control, digital power, and industrial automation—even small inefficiencies can impact real-time performance.
Common optimization techniques include:
- Reordering instructions to reduce data dependencies
- Avoiding unnecessary branches
- Using registers efficiently
- Leveraging parallel instruction capabilities where available
Conclusion
In the C28x (28x) DSP architecture, the main pipeline conflicts include:
- Data hazardscaused by instruction dependencies
- Resource conflictsdue to shared hardware usage
- Program flow (control) hazardsfrom branches and interrupts
- Memory access conflictsinvolving instruction and data fetches
Recognizing and minimizing these conflicts helps improve execution efficiency and ensures stable real-time performance in C28x-based systems.

COMMENTS