* Question
What coding structures for the Group of Pictures (GOP) does HEVC define to support different applications?
* Answer
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Background on GOP in HEVC
In video compression, the Group of Pictures (GOP) structure defines how frames are organized and referenced. It determines compression efficiency, random access capability, and latency. HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding, also known as H.265) adopts flexible GOP structures to accommodate a wide variety of application scenarios—from real-time video conferencing to high-quality broadcasting and video-on-demand.
2. Coding Structures in HEVC
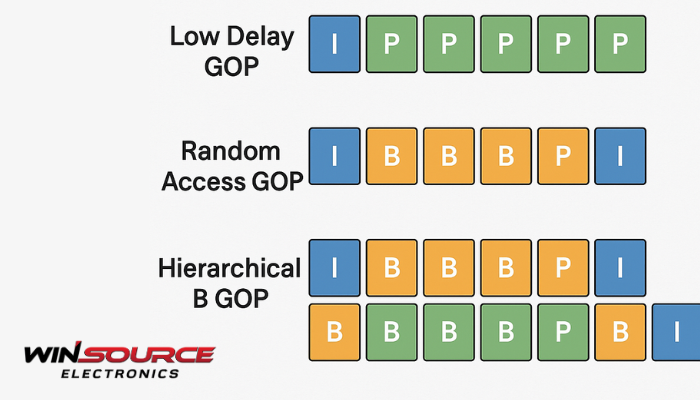
HEVC supports several GOP coding structures, each optimized for different trade-offs between compression efficiency, delay, and random access:
Low Delay GOP
Primarily uses I-frames and P-frames, with very limited use of B-frames.
Frames are coded in display order, minimizing buffering.
Suitable for real-time communication (e.g., video conferencing, live streaming).
Random Access GOP
Employs I-frames, P-frames, and B-frames with hierarchical prediction.
Provides better compression efficiency while still allowing periodic random access points.
Common in broadcasting and streaming applications where fast channel change or seeking is needed.
Hierarchical B GOP
Extensive use of bi-directional (B) frames, arranged in a hierarchical prediction tree.
Achieves the highest compression efficiency, but with higher latency.
Well-suited for storage and video-on-demand services, where low delay is not critical but bit-rate savings are important.
3. Flexibility of HEVC GOP
HEVC does not enforce a single GOP structure. Instead, it allows encoders to configure GOP length, frame types, and prediction hierarchy depending on the application’s requirements. This flexibility makes HEVC adaptable to both low-latency interactive applications and high-efficiency non-real-time applications.
Summary
HEVC defines flexible GOP coding structures—Low Delay, Random Access, and Hierarchical B—to balance between latency, compression efficiency, and random access.
Low Delay GOP → suited for interactive and real-time use.
Random Access GOP → optimized for broadcast and streaming.
Hierarchical B GOP → delivers maximum efficiency for offline storage and VOD.

COMMENTS