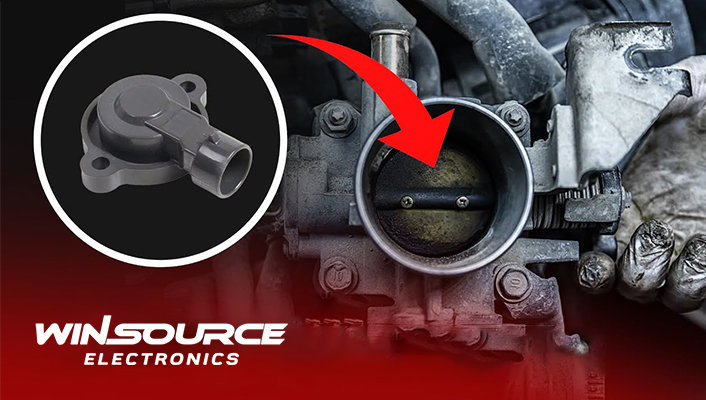
A Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is a vital component that monitors the air intake of an engine. Its primary function is to monitor the position of the throttle closely. Typically, the TPS is mounted on the butterfly spindle or shaft to provide immediate throttle position feedback.
Some advanced sensor designs are also utilized for this purpose. Today, we will talk about the types and working principles of throttle position sensors.
Table of Contents
ToggleThrottle Position Sensor Types
Three types of conventional position sensors are used in throttle position sensing: sliding resistance integration position sensors, idle switching position sensors, and position sensors.
However, the latest innovation in intelligent throttle shaft door control systems incorporates linear double Hall sensors and double sliding resistance sensors as throttle position sensors.
The primary sensor used in engine electrical control systems nowadays is the throttle position sensor with Hall components and double slide resistance sensors. Toyota Camry, Carolla, and other vehicles utilize Hall sensors, while Nissan Scorpio and General Excelle rely on double sliding resistance sensors.
1. Hall Throttle Position Sensor
The 2016 Toyota Camry Mixed Power Model (Engine Model 6Ar-FSE) features a non-contact Double Hall element throttle position sensor.
Its components consist mainly of magnets located on the throttle axis that can rotate around the Hall element, which is a key part of this sensor.
2. Slide Resistance Throttle Position Sensor
Also known as the linear output throttle position sensor, the variable resistive throttle position sensor, and the potential ribbon throttle position sensor, the slide resistance throttle position sensor is being widely adopted by various automobile manufacturers. Many vehicles now incorporate twin variable resistance throttle position sensors.
Working Principle of Throttle Position Sensor
The throttle position sensor, also known as a throttle opening sensor or throttle switch, is crucial in determining the engine’s operating state. Its primary function is to identify whether an engine is under load or idle, enabling fuel level adjustments or conducting oil-oil management.
The sensor consists of one variable resistor as well as multiple switches set up on the body of the throttle. These switches have two contacts, one for full open and one for idle. While the throttle is idling, the idle contact is closed, sending a signal to the computer indicating the idle operating condition.
However, while the throttle moves to a different position, the idling contact opens, and the sensor outputs a voltage signal proportional to the throttle’s various angles.
By analyzing the value of the voltage, the computer can determine the load on the engine. A significant change in the voltage of the signal over a specific duration indicates either acceleration or slowdown in the engine’s operating state.
The computer then utilizes this operational data to make necessary adjustments in fuel levels or conduct oil-oil management.
Conclusion
The throttle position sensor is critical to a vehicle’s engine management system. It monitors the position of the throttle and provides real-time data to the engine control unit, allowing for precise fuel delivery and efficient power output.
This helps to ensure optimal engine performance and can contribute to a smoother driving experience and improved fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of a faulty throttle position sensor are essential for maintaining the proper functioning of the engine management system. And if you are interested in purchasing throttle position sensors in bulk, please contact us here at WIN SOURCE.

COMMENTS