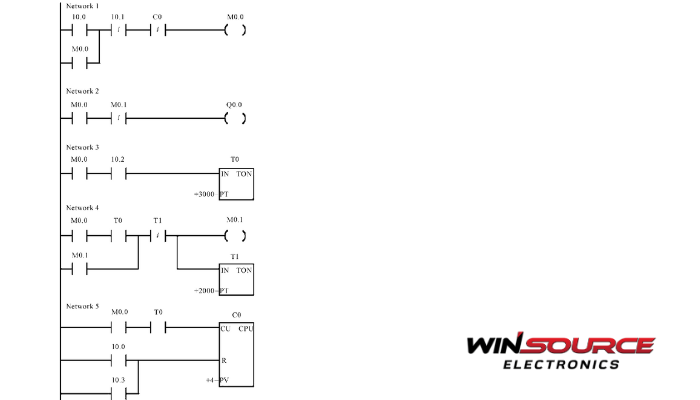
* Question
What are the characteristics of ladder diagrams?
* Answer
Here are the key characteristics of ladder diagrams, especially in the context of industrial control systems and PLC programming:
Table of Contents
ToggleCharacteristics of Ladder Diagrams
1. Graphical and Intuitive Format
Resembles a ladder with two vertical rails and multiple horizontal “rungs”.
Each rung represents a logical control operation.
The layout mimics electrical relay control circuits, making it easy for electricians and automation engineers to understand.
2. Logic-Based Programming
Implements Boolean logic (AND, OR, NOT) using symbols such as:
Normally open/closed contacts (inputs or conditions)
Coils (outputs or actuators)
Other logic elements include timers, counters, and latches.
3. Sequential Execution
Executed by the PLC top-to-bottom, left-to-right on each rung.
Each rung is evaluated during every PLC scan cycle.
Outputs are updated based on the state of inputs and logic.
4. Modular and Expandable
Each rung is independent, which makes the program:
Easy to modify
Easy to expand
Easy to troubleshoot
5. Real-Time and Deterministic
Designed for real-time control tasks.
Ensures predictable and repeatable execution, which is essential for safety-critical systems.
6. Hardware-Oriented
Designed to directly interface with PLC inputs and outputs.
Reflects the wiring logic of physical control panels.
Often used in industrial automation, process control, and machine operations.
7. Readable by Non-Programmers
Since ladder diagrams are based on electrical schematics, they can be interpreted by people without software engineering backgrounds—especially those from maintenance or operations roles.
Summary Table
Feature | Description |
Visual format | Ladder-like structure with rails and rungs |
Logic representation | Boolean logic using contacts, coils, timers, etc. |
Execution order | Top-to-bottom, left-to-right |
Modularity | Each rung is independent and easy to modify |
Hardware compatibility | Interfaces directly with PLC hardware and industrial equipment |
User-friendly | Accessible to technicians and non-programmers familiar with relay diagrams |

COMMENTS