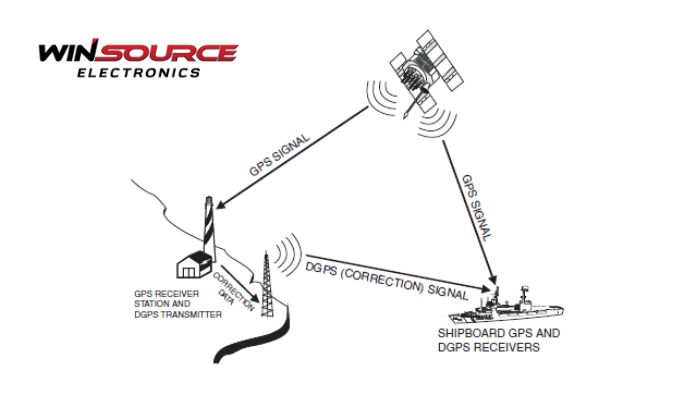
* Question
What are the components of the GPS satellite positioning system?
* Answer
The GPS (Global Positioning System) satellite positioning system consists of three major segments, each with distinct roles and components. Together, these segments work in coordination to provide accurate location, velocity, and time information anywhere on Earth.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Space Segment
This segment consists of the constellation of GPS satellites orbiting the Earth.
Key Components:
GPS Satellites (Space Vehicles or SVs):
Typically, at least 24 active satellites (with spares) orbit at ~20,200 km altitude in six orbital planes.
Each satellite continuously transmits:
Navigation data (ephemeris and almanac).
Precise timing signals generated by onboard atomic clocks.
Atomic Clocks:
Cesium and rubidium clocks provide nanosecond-level precision.
Radio Transmitters:
Operate primarily on L1 (1575.42 MHz), L2 (1227.60 MHz), and L5 (1176.45 MHz) bands.
Function:
Provide global coverage by broadcasting positioning and timing signals to Earth.
2. Control Segment
Also known as the Ground Control Segment, this manages the operation, health, and accuracy of the satellite constellation.
Key Components:
Master Control Station (MCS):
Located at Schriever Space Force Base, Colorado.
Oversees the system, computes satellite ephemeris and clock corrections.
Monitor Stations (globally distributed):
Receive GPS signals from satellites to monitor performance.
Provide tracking data back to the MCS.
Ground Antennas:
Send commands and updates to satellites.
Maintain synchronization and adjust satellite orbits as needed.
Function:
Ensure satellites remain in proper orbit and deliver accurate timing/position data.
3. User Segment
This is the portion of the system used by civilians and military users for navigation and positioning.
Key Components:
GPS Receivers:
Devices found in smartphones, vehicles, aircraft, ships, military equipment, etc.
Use triangulation (more precisely, trilateration) from multiple satellites to compute position.
Processing Unit:
Computes location using time delay of received satellite signals.
Antenna:
Captures signals from multiple satellites.
Function:
Receives and decodes satellite signals to determine the user’s position, velocity, and time (PVT) solution.
Summary Table
Segment | Key Components | Main Functions |
Space Segment | Satellites, atomic clocks, transmitters | Broadcast positioning and timing signals |
Control Segment | MCS, monitor stations, ground antennas | Satellite control, data correction, system monitoring |
User Segment | GPS receivers, antennas, processors | Receive signals and compute location and time |
Conclusion:
The GPS system is a tightly coordinated infrastructure involving orbiting satellites, ground-based control stations, and end-user devices. Its high precision and global availability make it indispensable for navigation, mapping, agriculture, aviation, and countless other applications across both civilian and military domains.

COMMENTS